Designing High Availability Configurations
High Availability (HA) configurations in Jive ensure service continuity by leveraging redundant and load-balanced nodes in either a single or multiple data center setup. Below is an overview of each configuration type:
Single Data Center HA Configuration
The single data center HA configuration guarantees availability through the use of redundant nodes for the web application, cache, document conversion, and databases, all physically located in the same data center.
Note: You may choose to configure redundant databases and replicate data between them. Jive does not provide database replication configuration or support. Your data center or DBA team, or both, must provide database support for you and your configuration. We have seen customers successfully deploy Oracle RAC and SQL Server HA configurations with Jive.
Example Configuration
Here is how a single data center HA configuration might look (your configuration may vary):
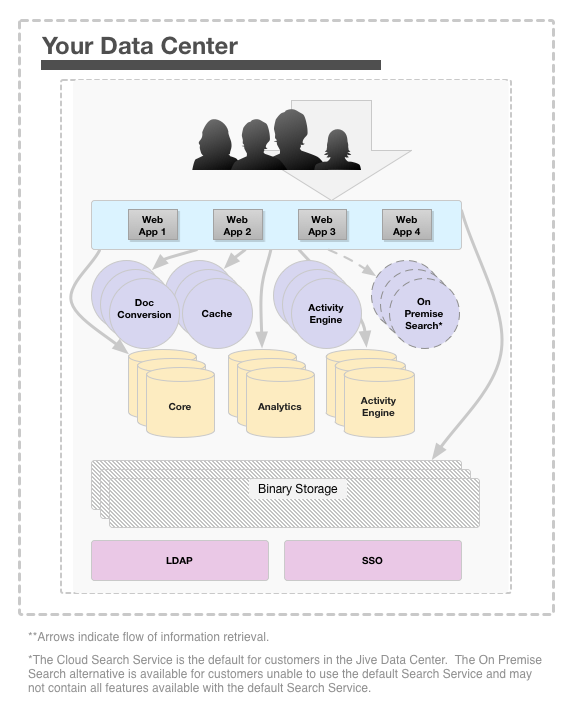
In this setup, web application nodes are configured in a cluster and deployed behind a load balancer, preferably an enterprise-grade load balancer, such as the F5 BIG-IP. For more information on setting up a cluster, see Clustering in Jive. Most customers deploy multiple web application nodes, usually three or more, in a single data center configuration.
Alternatively, you could deploy additional web application nodes in the cluster as passive participants, which remain online and standby, available to come online if necessary. For example, the Jive application may be running on these nodes, but not serving requests.
Multiple Data Center HA Configuration
The multiple data centers HA configuration ensures availability across geographically-distributed and redundant Jive platforms as an active or passive configuration. Please note that you cannot have Jive running in multiple data centers simultaneously.
Example Configuration
Here is how a multiple data center HA configuration might look (your configuration may vary):
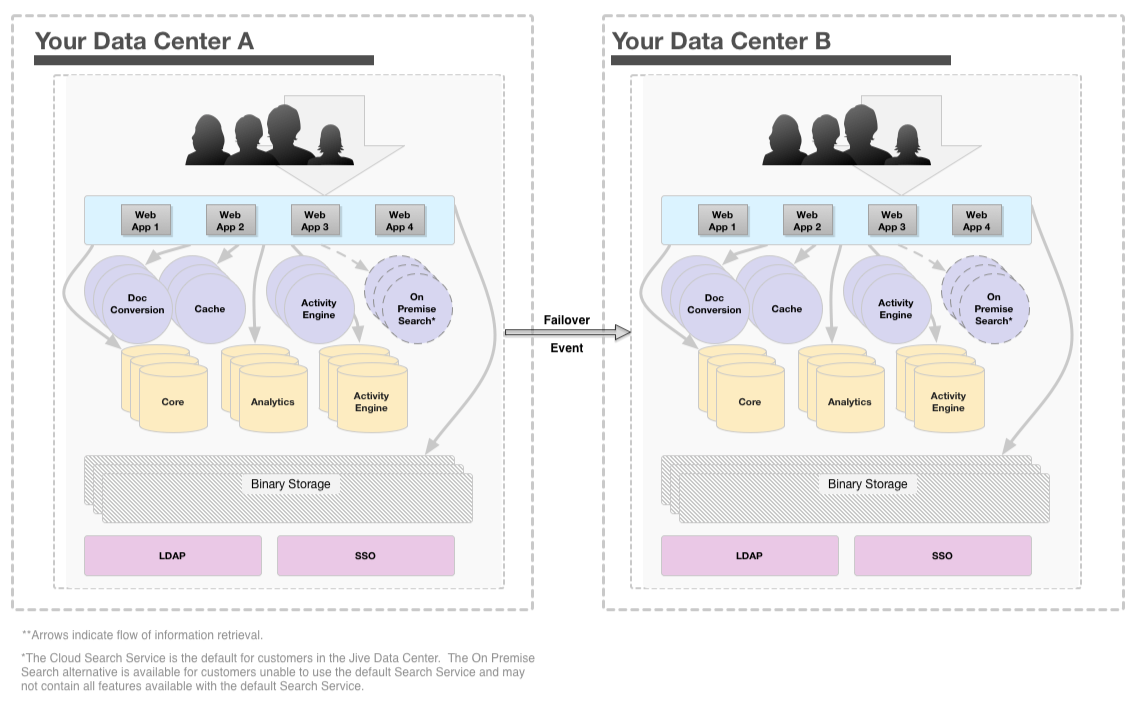
In this configuration, web application nodes are also configured in a cluster and deployed behind a load balancer, preferably an enterprise-grade load balancer such as the F5 BIG-IP. For more information on cluster setup, refer to Clustering in Jive.
In the passive standby data center system, the web application nodes can be booted up at the operating system level but not running the Jive application while the active production data center is operating. Meanwhile, cache nodes, Document Conversion service nodes, Activity Engine nodes, and database nodes in the passive standby data center may remain powered on.
The web application nodes in the passive standby data center cannot be up and available all the time. If you attempted to maintain their availability, they would communicate with the active production cluster as if they were part of it, potentially resulting in catastrophic issues in your production cluster.
For information on how to bring up Data Center B in the event of a failure, see Starting up after failover.
Common Notes for Both Configurations
-
Database Redundancy: In both configurations, you may choose to configure redundant databases and replicate data between them. Jive does not provide database replication configuration or support; this must be handled by your data center or DBA team.
-
Enterprise-Grade Load Balancers: Both configuration types prefer the use of enterprise-grade load balancers for improved performance and reliability.